(Beta) EVA Calculations when Dated Resource Rates Apply
For full details of when Estimates Versus Actuals records (EVAs) are generated, see Estimates Versus Actuals. This page uses examples to illustrate how estimated and actual values are calculated on EVAs when dated resource rates are being used by assignments and their related timecards.
For an introduction to dated resource rates, see (Beta) Dated Resource Rates Overview.
Example Scenario
An assignment starts on September 15, 2025 and ends on October 10, 2025. Its schedule specifies five hours worked daily Monday - Friday, and no hours worked Saturday - Sunday. This means that the total working hours per week is 25.
The assignment is using a bill rate card with the following dated resource rates:
| Effective Date | Rate |
|---|---|
| September 1, 2025 | $100 |
| September 24, 2025 | $120 |
Calculation of Estimated Values
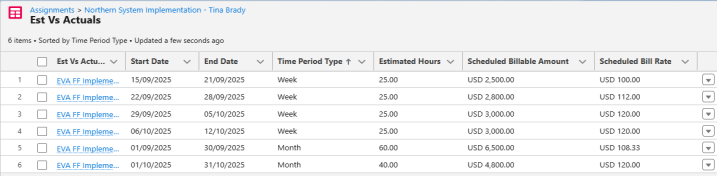
The following table shows the rate that applies each day of the assignment, and how scheduled EVA values are calculated using that information.
| Month | Date | Rate | Scheduled Hours | Scheduled Billable Amount | Scheduled Bill Rate (Amount / Hours) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| September 2025 | 15 Monday | 100 | 5 | 500 | |
| 16 Tuesday | 100 | 5 | 500 | ||
| 17 Wednesday | 100 | 5 | 500 | ||
| 18 Thursday | 100 | 5 | 500 | ||
| 19 Friday | 100 | 5 | 500 | ||
| Week 1 Total | 25 | 2,500 | 2,500 / 25 = 100 | ||
| 22 Monday | 100 | 5 | 500 | ||
| 23 Tuesday | 100 | 5 | 500 | ||
| 24 Wednesday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| 25 Thursday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| 26 Friday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| Week 2 Total | 25 | 2,800 | 2,800 / 25 = 112 | ||
| 29 Monday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| 30 Tuesday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| October | 1 Wednesday | 120 | 5 | 600 | |
| 2 Thursday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| 3 Friday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| Week 3 Total | 25 | 3,000 | 3,000 / 25 = 120 | ||
| 6 Monday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| 7 Tuesday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| 8 Wednesday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| 9 Thursday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| 10 Friday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| Week 4 Total | 25 | 3,000 | 3,000 / 25 = 120 | ||
| September Total | 60 | 6,500 | 6,500 / 60 = 108.33 | ||
| October Total | 40 | 4,800 | 4,800 / 40 = 120 | ||
When EVAs are generated for this assignment, the scheduled values are as shown:
Calculation of Actual Values
By default, actual EVA values are calculated when timecards are submitted or approved.
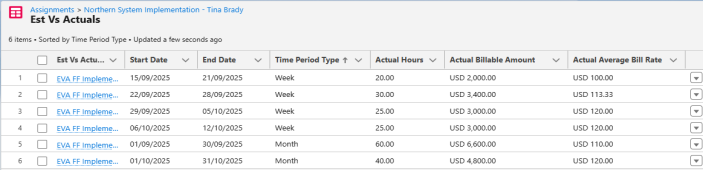
The following table shows how actual EVA values are calculated for the assignment in the previous table. Timecards are submitted for the hours shown in the Actual Hours column. Notice that no hours are worked on September 19. To make that time up, 2.5 extra hours are worked on both September 24 and September 25.
| Month | Date | Rate | Actual Hours | Actual Billable Amount | Actual Average Bill Rate (Amount / Hours) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| September 2025 | 15 Monday | 100 | 5 | 500 | |
| 16 Tuesday | 100 | 5 | 500 | ||
| 17 Wednesday | 100 | 5 | 500 | ||
| 18 Thursday | 100 | 5 | 500 | ||
| 19 Friday | 100 | 0 | 500 | ||
| Week 1 Total | 20 | 2,000 | 2,000 / 20 = 100 | ||
| 22 Monday | 100 | 5 | 500 | ||
| 23 Tuesday | 100 | 5 | 500 | ||
| 24 Wednesday | 120 | 7.5 | 900 | ||
| 25 Thursday | 120 | 7.5 | 900 | ||
| 26 Friday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| Week 2 Total | 30 | 3,400 | 3,400 / 30 = 113.33 | ||
| 29 Monday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| 30 Tuesday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| October | 1 Wednesday | 120 | 5 | 600 | |
| 2 Thursday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| 3 Friday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| Week 3 Total | 25 | 3,000 | 3,000 / 25 = 120 | ||
| 6 Monday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| 7 Tuesday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| 8 Wednesday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| 9 Thursday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| 10 Friday | 120 | 5 | 600 | ||
| Week 4 Total | 25 | 3,000 | 3,000 / 25 = 120 | ||
| September Total | 60 | 6,600 | 6,600 / 60 = 110 | ||
| October Total | 40 | 4,800 | 4,800 / 40 = 120 | ||
Now when EVAs are generated for the assignment, the actual values are as shown:
When you compare both scheduled and actual values, you can see that the actual values for weeks 1 and 2, and for the month of September, are different from the scheduled values. This is because no hours were worked on September 19 when the rate was $100. Instead, 2.5 extra hours were worked on both September 24 and September 25 when the rate was $120.
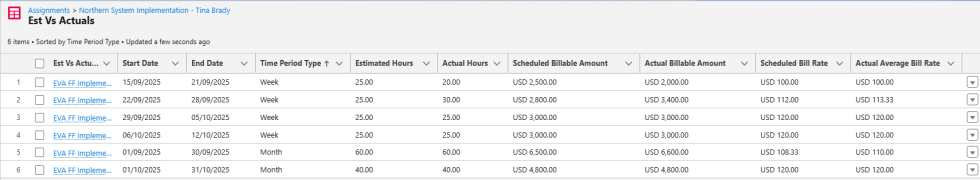
This illustrates that when hours are moved to after the rate increase, the actual billable amount is greater than the estimated amount because more hours are worked at the higher rate. Moving hours to before the rate increase would have resulted in the actual billable amount being less than the estimated amount because more hours would have been worked at the lower rate.
 SECTIONS
SECTIONS