The "Equal Split" revenue recognition method is also sometimes called the Ratable recognition method and relates to fixed fee projects and milestones.
A revenue forecast record is created for each monthly time period to store the values for these objects for use in Revenue Forecasting.
 Integration with Revenue Management
Integration with Revenue Management
If you are using the integration between PSA and Revenue Management, records looking up to a template of type "Equal Split" that fall within the monthly time periods spanning the project start and end dates are included.
If you run Revenue Forecasting after revenue has been recognized, the revenue is displayed in the Revenue Recognized to Date field on the revenue forecast record for the monthly time period that corresponds to the date the revenue was recognized in Revenue Management.
 No Integration with Revenue Management
No Integration with Revenue Management
If you are not using the integration between PSA and Revenue Management, Revenue Forecasting looks at the Recognition Method field on a project or milestone record, which must contain one of the "Equal Split" options, such as "Equal Split: 4,4,5".
Calculating Duration
PSA uses the project or milestone duration to calculate revenue forecasts for the "Equal Split" recognition method.
Project
The duration of a project is calculated using the Start Date and End Date fields on the project record.
Milestone
The duration of a milestone is calculated using the following fields on the milestone record.
|
Field |
Notes |
|---|---|
| Start Date | If the date in this field falls before the project start date, after the project end date, or if this field does not contain a value, the date in the Start Date field on the project record is used. |
| Actual Date |
If the date in this field falls before the project start date or after the project end date, the date in the End Date field on the project record is used. If this field does not contain a value, the date in the Target Date field on the milestone record is used. |
| Target Date | If the date in this field falls before the project start date or after the project end date, the date in the End Date field on the project record is used. |
Calculating the Split Amount for Full Periods
If you are using the "Equal Split: Months/Part Periods" recognition method, when the duration of a project or milestone consists of full periods, such as full months, the total scheduled revenue is split equally between those periods.
If you are using the "Equal Split: Months" or "Equal Split: 4,4,5" recognition method, the revenue is split equally between the monthly periods. These periods do not have to be full periods.
 Example: January 1 to March 31
Example: January 1 to March 31
The project or milestone spans three months. As all periods are full periods, the calculation is based on three months.
Total scheduled revenue over the project or milestone duration = $30,000.
The revenue is split in the following way.
| Month | Calculation |
Amount $ |
|---|---|---|
| January | 30,000/3 | 10,000 |
| February | 30,000/3 | 10,000 |
| March | 30,000/3 | 10,000 |
Calculating the Split Amount for Part Periods
This information in this section applies if you are using the "Equal Split: Months/Part Periods" recognition method.
If the start period within the project or milestone duration is a part period:
- The number of months is calculated as the number of calendar months spanning the project or milestone duration minus one month.
- One month's revenue is split between the start period and the end period.
Monthly revenue is calculated as the total scheduled revenue divided by the number of months. The number of days in a month is not relevant to this calculation. For example, February (28 or 29 days) is allocated the same monthly revenue as March (31 days).
The revenue for the start part period is calculated as:
(Number of days in start part period/Total days in start time period) * Monthly revenue
The revenue for the end period, which is not necessarily a part period, is calculated as:
Monthly revenue - Revenue for start part period
The sum of the revenue in the start period and the end period adds up to one full month's revenue.
 Example 1: June 3 to October 28 (Start and End Part Periods)
Example 1: June 3 to October 28 (Start and End Part Periods)
The project or milestone spans five months. As the start period is a part period, the calculation is based on four months, with one month to be split between the start and end part periods.
Days in start part period: June 3 to June 30 = 27 days.
Total scheduled revenue over the project or milestone duration = $40,000.
A full month's scheduled revenue is $40,000/4 = $10,000.
The revenue is split in the following way.
| Month | Calculation |
Amount $ |
|---|---|---|
| June (Start Part Period) | (27 days/30 days) * (40,000/4) | 9,000 |
| July | 40,000/4 | 10,000 |
| August | 40,000/4 | 10,000 |
| September | 40,000/4 | 10,000 |
| October (End Part Period) | 10,000 - 9,000 | 1,000 |
 Example 2: June 12 to October 31 (Start Part Period)
Example 2: June 12 to October 31 (Start Part Period)
The project or milestone spans five months. As the start period is a part period, the calculation is based on four months, with one month to be split between the start and end periods.
Days in start part period: June 12 to June 30 = 18 days.
Total scheduled revenue over the project or milestone duration = $40,000.
A full month's scheduled revenue is $40,000/4 = $10,000.
The revenue is split in the following way.
| Month | Calculation |
Amount $ |
|---|---|---|
| June (Start Part Period) | (18 days/30 days) * (40,000/4) | 6,000 |
| July | 40,000/4 | 10,000 |
| August | 40,000/4 | 10,000 |
| September | 40,000/4 | 10,000 |
| October (End Period) | 10,000 - 6,000 | 4,000 |
 Example 3: June 1 to October 28 (End Part Period)
Example 3: June 1 to October 28 (End Part Period)
The project or milestone spans five months. As the start period is not a part period, the calculation is based on five months.
Total scheduled revenue over the project or milestone duration = $40,000.
The start period is not a part period, which means it has a full month's scheduled revenue. The end period would normally take the remainder of a month's revenue after the amount for the start period had been deducted. Because the start period is not a part period, nothing is deducted and the end period takes the full monthly amount.
The scheduled revenue is split in the following way.
| Month | Calculation |
Amount $ |
|---|---|---|
| June (Start Period) | 40,000/5 | 8,000 |
| July | 40,000/5 | 8,000 |
| August | 40,000/5 | 8,000 |
| September | 40,000/5 | 8,000 |
| October (End Part Period) | (40,000/5) | 8,000 |
 Example 4: January 11 to February 22 (Start and End Part Periods, No Full Periods)
Example 4: January 11 to February 22 (Start and End Part Periods, No Full Periods)
The project or milestone spans two months, which are both part periods.
Days in start part period: January 11 to January 31 = 20 days.
Total scheduled revenue over the project or milestone duration = $6,200.
The scheduled revenue is split in the following way.
| Month | Calculation |
Amount $ |
|---|---|---|
| January (Start Part Period) | (20 days/31 days) * 6,200 | 4,000 |
| February (End Part Period) | 6,200 - 4,000 | 2,200 |
Calculating the Split Amount for Days
This information in this section applies if you are using the "Equal Split: Days" recognition method.
When you run a revenue forecast, daily revenue is calculated as:
Total scheduled revenue/Total days in the project or milestone duration
The monthly revenue is calculated as:
Daily revenue * Number of days in monthly time period within the project or milestone duration
This means, for example, if your project or milestone starts on March 4, there will be 28 days’ worth of revenue for that month.
 Example
Example
A project spans 82 days, as it runs from March 4 to May 24.
Total scheduled revenue over the project or milestone duration = $8,200.
Daily revenue is 8,200/82 days = $100.
The scheduled revenue is split in the following way for each monthly time period.
| Month |
No of Days in Project Duration |
Calculation |
Amount $ |
|---|---|---|---|
| March | 28 | (28 days/82 days) * 8,200 | 2,800 |
| April | 30 | (30 days/82 days) * 8,200 | 3,000 |
| May | 24 | (24 days/82 days) * 8,200 | 2,400 |
Calculating with Closed Periods
This section explains how the revenue forecasts are calculated when relevant records are marked as "Equal Split" and there are closed time periods within the project or milestone duration.
 Integration with Revenue Management
Integration with Revenue Management
If you are using the integration between PSA and Revenue Management and you run a revenue forecast, the revenue is treated in the following way when there are closed monthly time periods:
- Closed period, full amount recognized: the full amount is displayed in the Revenue Recognized to Date field on the revenue forecast record for the closed time period.
- Closed period, partial amount recognized: the part that has been recognized is displayed in the Revenue Recognized to Date field on the revenue forecast record for the closed time period. The remainder is displayed in the Revenue Pending Recognition field on the revenue forecast record for the next open time period.
If there are no open time periods within the project or milestone duration, the revenue pending recognition is moved forward until Revenue Forecasting finds an open time period:
- First open period: a revenue forecast record is created for the next available open time period and the revenue is displayed in the Revenue Pending Recognition field on this record. If the revenue is subsequently recognized and you run Revenue Forecasting again, the revenue is moved into the Revenue Recognized to Date field on the revenue forecast record for the time period that corresponds to the date the revenue was recognized in Revenue Management.
- Open period that is not the first open period: a revenue forecast record is created for the open time period and the revenue is displayed in the Scheduled Revenue field on this record.
 No Integration with Revenue Management
No Integration with Revenue Management
If you are not using the integration between PSA and Revenue Management and you run a revenue forecast, the revenue is treated in the following way when there are closed monthly time periods:
- Closed period: revenue is displayed in the Revenue Pending Recognition field on the revenue forecast record for the closed period.
- First open period: revenue is displayed in the Revenue Pending Recognition field on the revenue forecast record for the relevant time period.
- Open period that is not the first open period: revenue is displayed in the Scheduled Revenue field on the revenue forecast record for the relevant time period.
revenue forecast
Example for Equal Split Recognition Method
 An active fixed fee project has the following attributes:
An active fixed fee project has the following attributes:
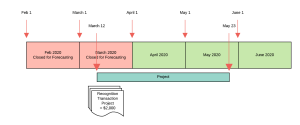
- Start Date = March 12.
- End Date = May 23.
- Bookings = $7,500.
- Recognition Method = Equal Split: Months.
- The monthly time period records for February and March have the Closed for Forecasting checkbox set to true.
The following diagram gives details of the dates, time periods, and records included in the forecast.
When Revenue Forecasting is run on the project, the following fields are updated on the revenue forecast records relating to each monthly time period.
|
Field |
$ Revenue | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| March | April | May | |
| Revenue Recognized To Date | $2,000 | $0 | $0 |
| Revenue Pending Recognition | $0 | $3,000 | $0 |
| Scheduled Revenue | $0 | $0 | $2,500 |
| Unscheduled Revenue (not applicable) | $0 | $0 | $0 |
The following revenue forecast type records are created.
| $ Value in Revenue Forecasting Fields | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue Source | Revenue Forecast Type | March |
April |
May |
| Equal Split: Project | Actual |
Revenue Recognized To Date: $2,000 Revenue Pending Recognition: $0 Scheduled Revenue: $0 Unscheduled Revenue: $0 |
Revenue Recognized To Date: $0 Revenue Pending Recognition: $3,000 Scheduled Revenue: $0 Unscheduled Revenue: $0 |
Revenue Recognized To Date: $0 Revenue Pending Recognition: $0 Scheduled Revenue: $8,000 Unscheduled Revenue: $0 |
| Equal Split: Project | Forecast |
Revenue Recognized To Date: $0 Revenue Pending Recognition: $0 Scheduled Revenue: $0 Unscheduled Revenue: $0 |
Revenue Recognized To Date: $0 Revenue Pending Recognition: $0 Scheduled Revenue: $0 Unscheduled Revenue: $0 |
Revenue Recognized To Date: $0 Revenue Pending Recognition: $0 Scheduled Revenue: $2,500 Unscheduled Revenue: $0 |
Notes
In March, only $2,000 out of an expected $2,500 was recognized. The remaining $500 rolls into the April time period, which is the next open period.
As April is the first open time period, the calculated $2,500 moves from Scheduled Revenue into Revenue Pending Recognition and is added to the $500 rolled over from March to give $3,000.
May contains the remaining $2,500 as scheduled. When the April time period is closed, this revenue will move into Revenue Pending Recognition.